Mycoses of the skin are common.They arise from infection with anthropophilic and zooanthropophilic fungi.You can become infected through personal contact when visiting public baths and saunas, swimming pools and fitness studios.Fungal pathologies have characteristic clinical manifestations, but not everyone knows what athlete's foot looks like, so few people seek medical help in the initial stages.This contributes to the spread of the infection.
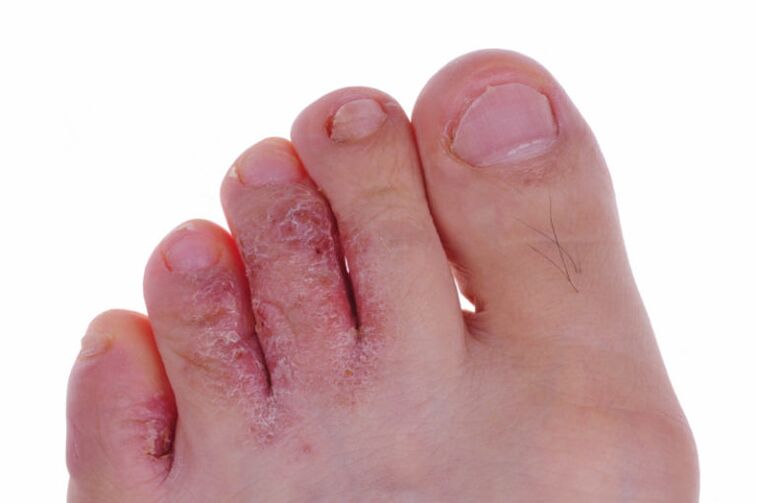
Symptoms of skin lesions on the toes
The initial changes caused by a fungal infection are difficult to notice: they do not cause pathological changes in the affected area and do not cause discomfort.If the immune system is strong, the infection can clear up on its own at this stage;With a decrease in the body's defenses, it will continue to develop and move on to the next phase.At this stage, flour-like detachments form in the interdigital area.The skin turns red, becomes dry and cracked.This process is accompanied by severe itching.The feet and heels look healthy.
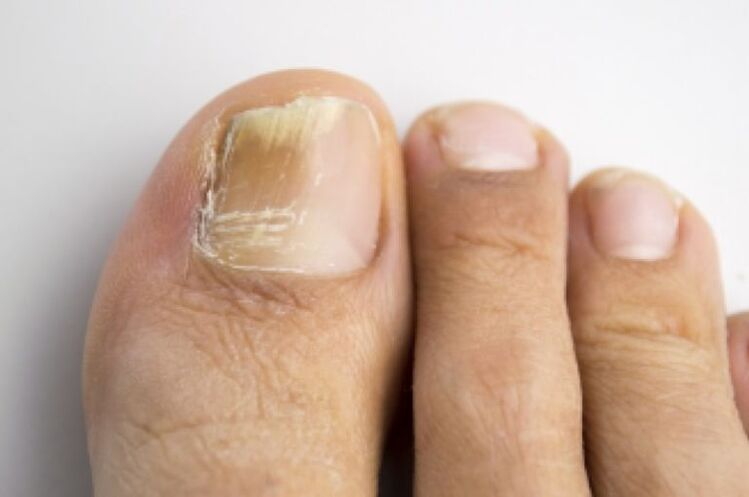
Symptoms of a fungal infection of the toenails
The affected nails have a specific appearance, so it is not difficult to recognize the beginning of an infection.The pathological process develops according to the following scenario:
- The nail plates thicken, their color changes: the pale pink hue disappears and a yellowish-gray color appears.
- A gap is created between the shaft and the plate.
- The nail plate gradually begins to peel off and its edges become brittle.They crumble and gradually collapse.
- There is severe itching in the affected area.It distracts you from everyday activities.
- Irritation and redness form on the skin between the fingers, then painful cracks appear.
- The affected area has an unpleasant sour smell.
It will be difficult to trim your nails with regular nail scissors.They cannot be processed with a nail file or special tweezers: the plates crumble.
Symptoms of a fungus on the soles of the feet
It's harder to recognize the signs of athlete's foot on your own.The development of infection leads to the appearance of formations on the sole that look like calluses.The appearance of further symptoms depends on which form of the disease progresses.
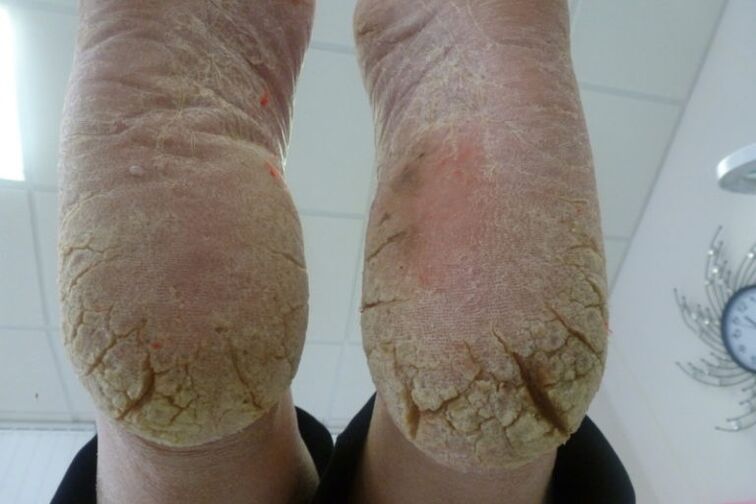
It all starts with the squamous cell carcinoma form.At this stage, the infection spreads to the entire sole.The skin on it becomes rough and calloused, begins to actively peel off and itch severely.Externally, the foot looks like the result of a lack of regular pedicure (unkempt).
The hyperkeratotic form develops next.Over time, gray thickenings form on the arches.They are flaking badly at the edges.Deep cracks appear in place of old calluses.This process causes severe pain.Doctors call this phenomenon “moccasin foot”.If you look at the sole of the affected foot from above, it looks as if there is a thick yellow-gray insole stuck there.The fungal infection spreads to the interdigital space and nails.They change color, peel off and collapse.
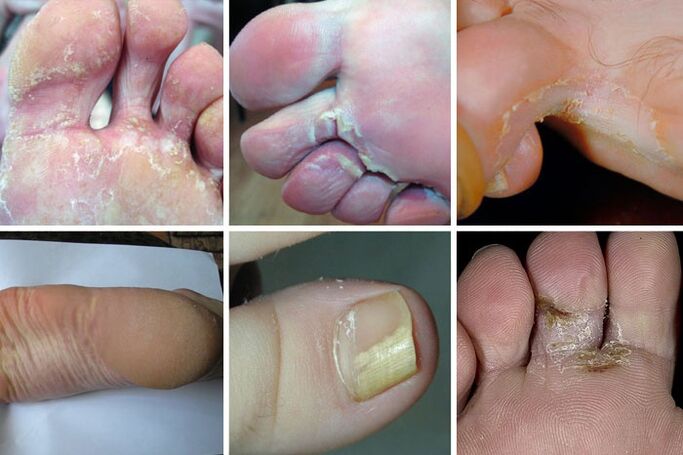
Dyshidrotic form.It is characterized by the appearance of blisters on the skin of the feet filled with a cloudy fluid.This is only possible with advanced forms of infection.When the bubbles collapse, weeping erosions form in their place and continually leak.Pathogenic bacteria easily penetrate open wounds.Secondary infection significantly worsens the patient's condition;In this case, it is very difficult to diagnose a fungal infection based on external manifestations: the symptoms are similar to the clinical picture of eczema or psoriasis.
Clinical signs of a fungus by stage of the disease
It can take 3-14 days from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms.The length of the incubation period largely depends on which type of fungus caused the development of characteristic symptoms (yeast, mold or Candida fungus) and on the state of the immune system.
A fungal infection goes through three stages in its development:
- At the initial stage, redness of the affected area, dry skin and peeling are observed.The patient feels mild itching.
- The middle stage is characterized by the spread of the infection to the entire foot.
- In advanced forms, damage to the nail plates occurs, the skin of the feet becomes riddled with cracks and the callous layer peels off in large layers.
If no etiotropic treatment is given, the infection progresses to the chronic stage.It is characterized by alternating remissions and exacerbations.
Differential diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease begins with an examination of the foot by a dermatologist and a medical history.Based on the results, the doctor prescribes additional laboratory tests.
Must be done:
- Scraping of the affected area and subsequent microscopy (with its help the fungal nature of the infection is confirmed).
- Sowing the extracted biological material in special nutrient media.Colonies of pathogenic microorganisms grown in this way make it possible to identify the causative agent of the disease and determine its sensitivity to modern antifungal drugs.Based on this laboratory test, a drug treatment regimen is drawn up.
Fungal skin infections must be differentiated from vitiligo, seborrhea, psoriasis, syphilitic leukoderma and neurodermatitis.For this purpose, examination of the skin under a Wood lamp and PCR are used.

How to fight athlete's foot
To combat a fungal infection are used:
- antifungal ointments;
- antifungals in tablet form;
- traditional medicine.
Ointments are applied to the affected areas twice a day;First, the skin of the feet must be steamed and the callus layer removed.The duration of taking the tablets is determined by the treating doctor.As a rule, treatment in the initial stages of infection lasts no more than a month;Advanced forms are treated within six months.Traditional medicine can significantly speed up the healing process.Doctors recommend their patients to take note of the following recipes.
Baths with vinegar and hydrogen peroxide.You need to pour water with a temperature of 37 degrees into a basin, add 20 grams of table vinegar, then put your feet in the water and warm them there for twenty minutes.After that, you need to remove the stratum corneum with pumice stone, wipe your feet dry and smear the affected skin areas with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.At the end of the procedure, the affected areas are lubricated with an antifungal cream prescribed by the doctor.
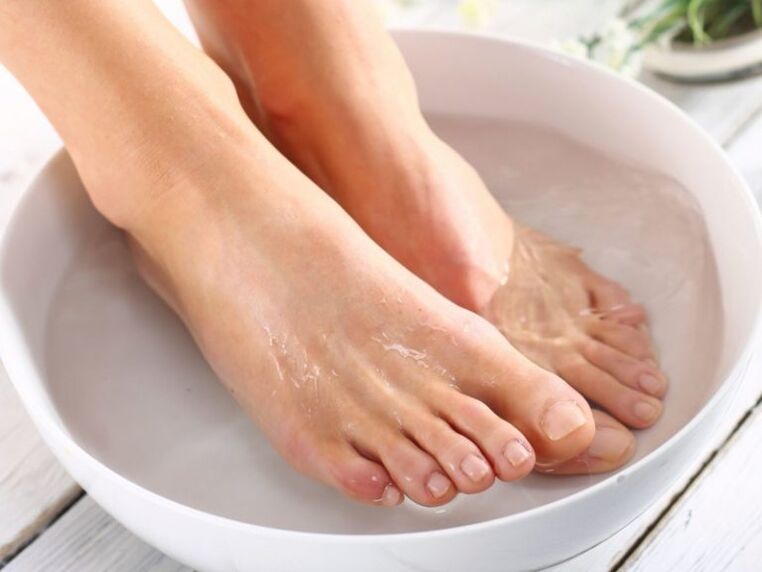

Salt baths and celandine juice.The feet are pre-steamed in a saline solution (a teaspoon per liter of water), and then lubricated with celandine juice made from fresh leaves and blades of grass.The procedure ends with the use of an antifungal drug.
Soda baths (20 grams of powder per two liters of water) can relieve inflammation and stimulate ulcer healing.The feet are steamed for fifteen minutes, wiped dry with a towel and treated with etiotropic ointment.
Throughout the treatment, it is important to thoroughly disinfect all surfaces that the sore feet come into contact with (shoes, clothing, bedding).After treating the affected areas of skin, you must wash your hands thoroughly and then treat them with a liquid antiseptic.Violation of the number of medications taken and their dosage leads to increased sensitivity of pathogenic microflora, which requires an extension of therapy and some changes to tablets and ointments.
To prevent relapses, it is important to prevent reinfection.Wear only dry shoes, choose socks made from natural fabrics, and use only personal pedicure accessories.



















